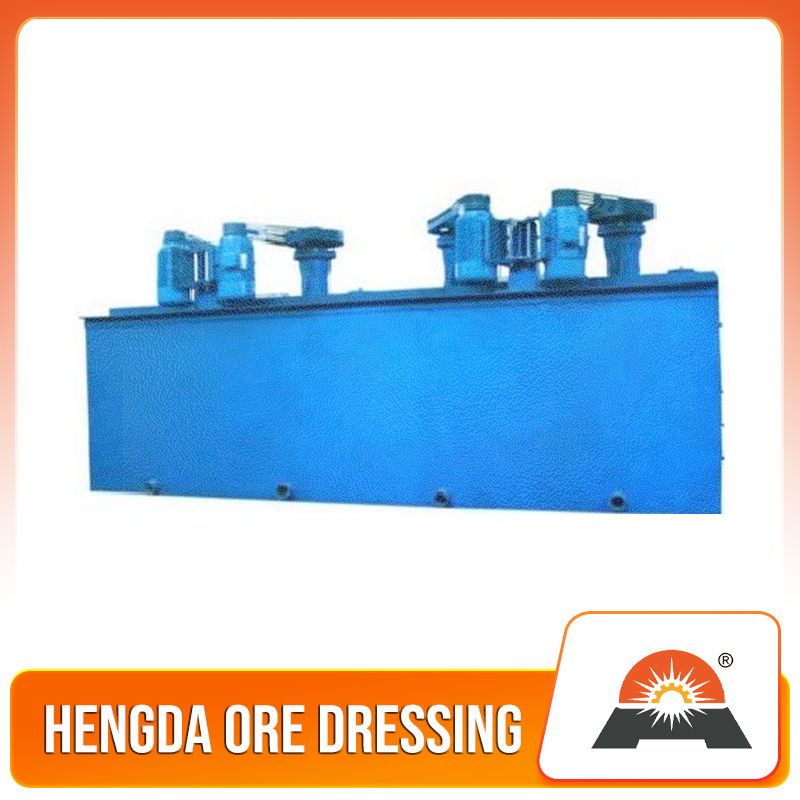
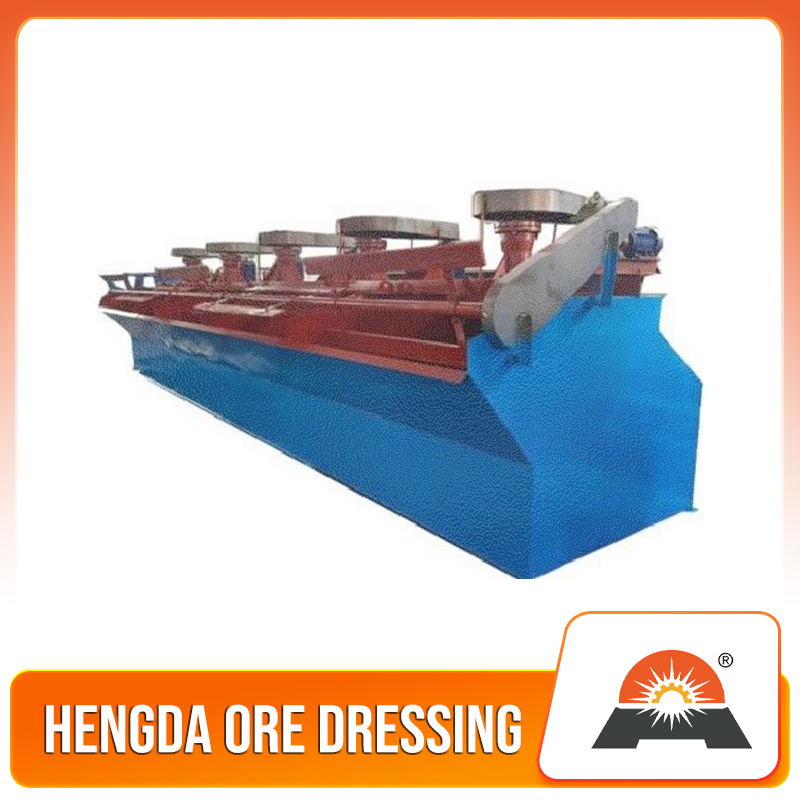
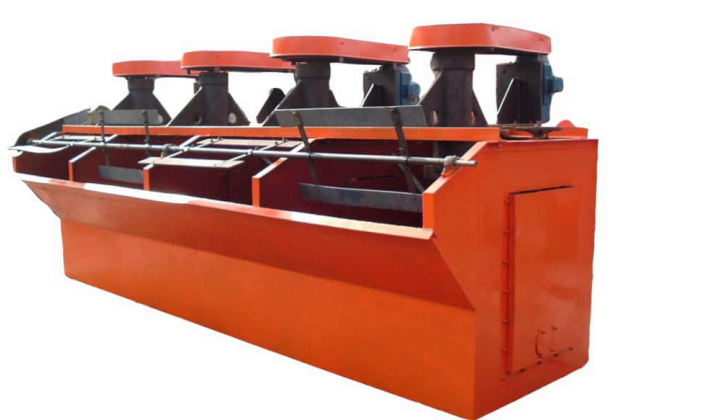
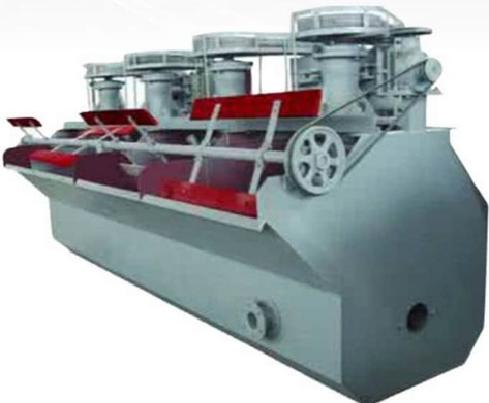
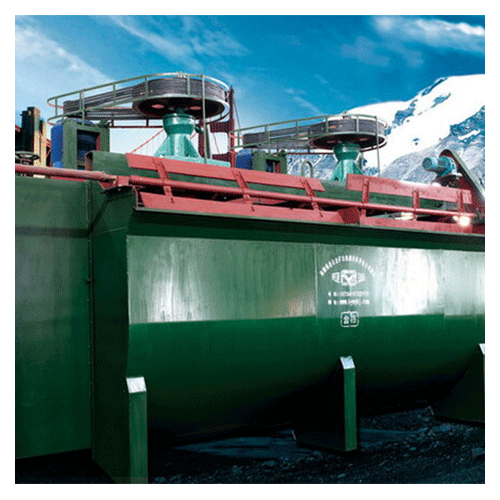
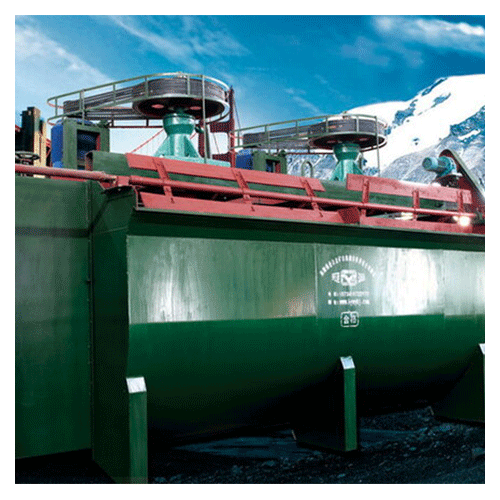
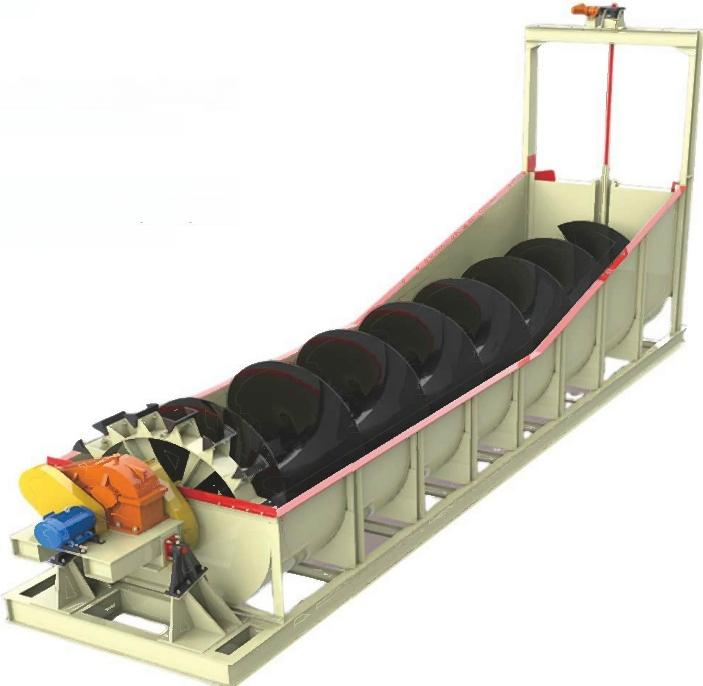
It is suitable for the separation of non-ferrous metals, ferrous metals, precious metals, and non-metallic minerals. The XCF type has self-prime slurry capacity and is called a suction tank; the KYF type has no self-priming slurry capacity, with lower power consumption than the XCF type, and is called a direct-flow tank. Generally, the XCF and KYF models are configured as a combined unit, arranged horizontally to facilitate process changes. The XCF/KYF flotation machine adopts a "U"-shaped tank body, hollow shaft aeration, and a suspended stator, especially a conical impeller with blades tilted backward at an angle. A porous cylindrical air distributor is installed in the impeller cavity, enabling air to be uniformly dispersed in most areas of the impeller blades, thus providing a larger slurry-air contact interface. When the XCF flotation machine operates, as the impeller rotates, the slurry in the tank is sucked into the space between the impeller blades from around the tank bottom through the lower end of the impeller. Meanwhile, low-pressure air supplied by a blower enters through the hollow shaft and the impeller's air distributor. After the slurry and air are fully mixed between the blades, the mixture is pushed obliquely upward from the upper half of the impeller, and then enters the entire tank after being stabilized and directed by the stator. Bubbles rise to the foam stabilization zone. After the enrichment process, the foam overflows spontaneously from the overflow weir into the foam tank. A portion of the slurry flows to the lower part of the impeller, which is then stirred by the impeller and remixed to form mineralized bubbles. The remaining slurry flows to the next tank and finally becomes tailings.
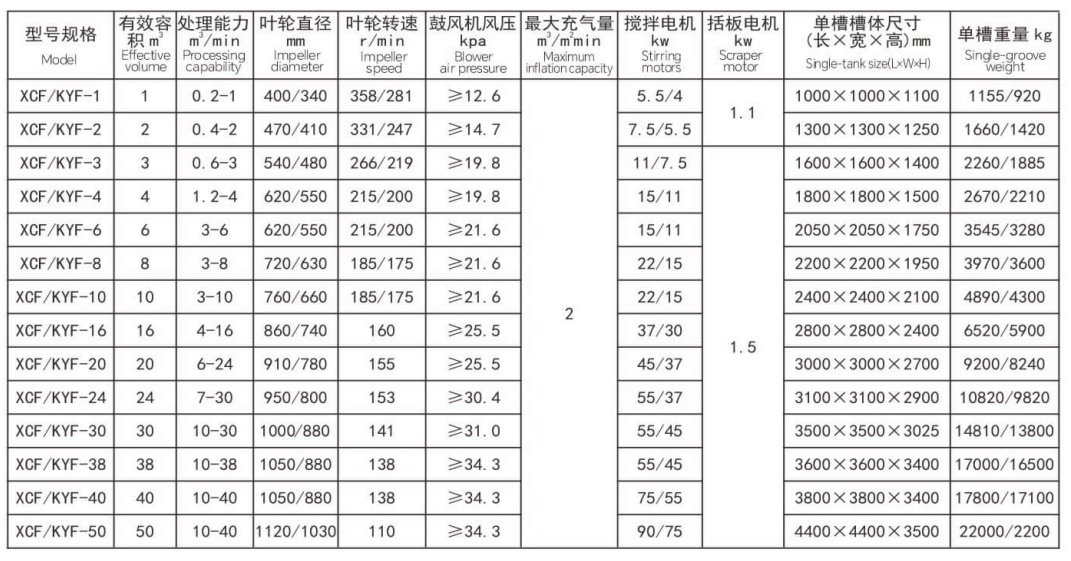
Main models and technical parameters